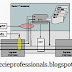
I know this is a fairly large set up but believe me it teach you
practically everything you need to know about LSAs and different ospf
area types. I have to admit this is not something I’ve created myself. I
stumbled upon this video on youtube http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7LzrvCvb-Ro&list=PLC6197249373E47E9 made
by one of the best network instructors out there Keith Barker and then
thought it would be great to lab it up and configure everything
with Keith.

I also thought of adding another ospf area number 3 and connect it to
area 1 where then we would have discontiguous areas ! and for a fix
we would have to use either GRE Tunnel or Virtual Link but as you can
see I did not do it just to avoid having too many devices to work with
and Virtual link and GRE Tunnel I will explain in another post.
Please go ahead and download following net file and build your topology
OSPF LSAs and Area Types
Please download following basic config , copy and paste them into relevant devices
basic_config_files
As a side note: if you’ve already visited my other post http://ccie4all.wordpress.com/2012/11/03/ccie_gns3_topology_/ and
managed to built you topology presented in CCIE GNS TOPOLOGY post then
YOU DO NOT have to use the files provided in this post and build the
topology from scratch cause you will easily be able to recreate above
set up once you’ve got CCIE GNS TOPOLOGY running on your machine. You
will have to use few subinterfaces on your routers , add few vlans on
switches but believe me it saves hell lot of time and most importantly
it teaches you many important configuration and troubleshooting skills
what you will have to face in yur R&S lab exam and the real world
also that way you only have one gns3 network on your PC that DOES IT
ALL for you
Check out this cisco tutorial about OSPF area types (although it does not explain the Not So Totally Stubby area)
http://www.cisco.com/E-Learning/bulk/public/ccnp/QLM_Configuring_OSPF_Special_Area_Types_BSCI/player.html
Thought it’d be good to add LSA types and various stub configuration.
Type 1 – Represents a router
Type 2 – Represents the pseudonode (designated router) for a multiaccess link
Type 3 – A network link summary (internal route)
Type 4 – Represents an ASBR
Type 5 – A route external to the OSPF domain
Type 7 – Used in stub areas in place of a type 5 LSA
Stub Areas
A stub area allows Type 2 and Type 3 LSAs. Type 5 LSAs are NOT
passed into the area. The ABR injects a type 3 LSA containing a default
route into the stub area.Filters the LSA-type 4 and 5.You will just have
inter-area routes inside this area (routes with the “IO” code)
ABR(config-router)#area 51 stub
ABR(config-router)#area 51 default-cost 10
Defines the cost of a default route sent into the stub area. Default is 1.
INTERNAL(config-router)#area 51 stub
- Note
All routers in the stub area must be configured with the area x stub command, including the Area Border Router (ABR). - Stub= No type 5 LSAs and default route
This is Cisco proprietary.Like stub areas, totally stubby areas do not receive type-3 , type-4 or type-5 LSAs from their ABRs . All routing out of the area relies on the single default route injected by the ABR
ABR(config-router)#area 51 stub no-summary
INTERNAL(config-router)#area 51 stub
- Note
Whereas all internal routers in the area are configured with the area x stub command, the ABR is configured with the area x stub no-summary command - Totally Stubby – ONLY Type 2 LSAs and default route
Not-So-Stubby Areas (NSSA)
This area is used when you are redistributing external routes. An NSSA makes use of type 7 LSAs, which are essentially type 5 LSAs in disguise. You will see “IO” routes (they are in the routing table because of the type-3 LSAs) also “N1/2″ routes which represents the NSSA area. This allows an ASBR to advertise external links to an ABR, which converts the type 7 LSAs into type 5 before flooding them to the rest of the OSPF domain.Type 3 LSAs will pass into and out of the area. Unlike a normal stub area, the ABR will NOT inject a default route into an NSSA unless explicitly configured to do so with
ABR(config-router)#area x nssa default-information originate
As traffic cannot be routed to external destinations without a default route, you’ll probably want to include above command.
ABR(config-router)#area 1 nssa
INTERNAL(config-router)#area 1 nssa
- Note
All routers in the NSSA stub area must be configured with the area x nssa command. - NSSA – Type 2, 3, and 7 LSAs with default route
Totally stub not-so-stubby area (totally NSSA)
This is Cisco proprietary.Filters type-3 ,type-4 and 5 LSAs, so inside the area you will only have a default route, besides the “N1/2″ routes that are normal on that type of area.
ABR(config-router)#area 11 nssa no-summary
INTERNAL(config-router)#area 11 nssa
- Note
Whereas all internal routers in the area are configured with the area x nssa command, the ABR is configured with the area x nssa no-summary command. - Totally NSSA – Only Type 2 and 7 LSAs and default route








0 comments:
Post a Comment